
Velocity & Vision: India Gears Up for 280 kmph Trains and Great Nicobar Transformation
By State Correspondents News Desk | February 17, 2026 | New Delhi
India’s infrastructure renaissance gains momentum with twin breakthroughs: the Ministry of Railways’ push for indigenous high-speed trains clocking 280 kmph and the National Green Tribunal’s (NGT) endorsement of the ambitious Great Nicobar mega project. These developments, announced amid Budget 2026’s rail focus, signal a self-reliant future under Atmanirbhar Bharat, blending cutting-edge rail tech with strategic island development.
Railway Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw revealed in Parliament that post-164 Vande Bharat successes, Integral Coach Factory (ICF) and BEML are prototyping next-gen trains. Meanwhile, NGT dismissed eco-challenges to the Rs 80,000 crore Nicobar initiative, stressing “strategic importance” and robust safeguards for biodiversity hotspots.
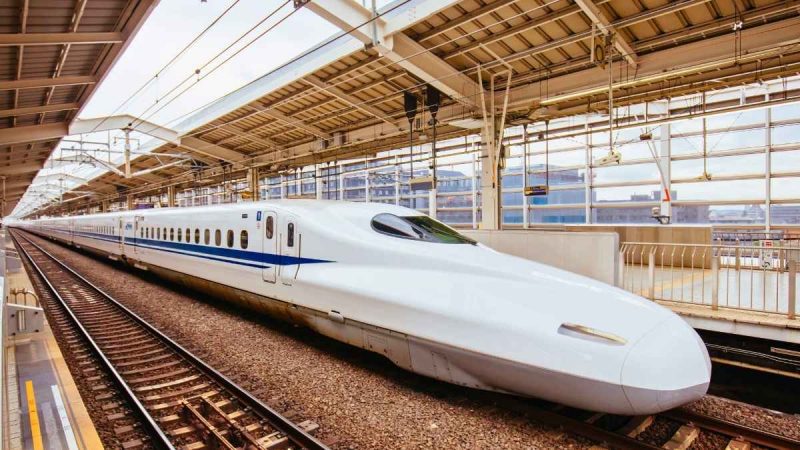
High-Speed Rail Revolution: 280 kmph Indigenous Marvels
The Rs 867 crore contract between Chennai’s ICF and Bengaluru’s BEML marks a pivot from import reliance. Two eight-coach sets, fully air-conditioned Chair Cars, boast reclining/rotatable seats, accessibility features, and infotainment—slated for Surat-Bilimora debut by late 2026.
Key Train Specs:
- Design Speed: 280 kmph (Operational: 250 kmph)
- Coach Cost: Rs 27.86 crore each
- Facilities: AC Chair Cars, Mobility Aids, Onboard Entertainment
- Build Site: BEML Bengaluru Complex
- First Route: Gujarat’s Surat-Bilimora Corridor
This aligns with seven new corridors—Delhi-Varanasi, Mumbai-Pune, etc.—spanning 4,000 km and Rs 16 lakh crore investments. Mumbai-Ahmedabad HSR progresses with 85% viaducts done, testing stretches operational soon. Standardization and manpower training ensure scalability.
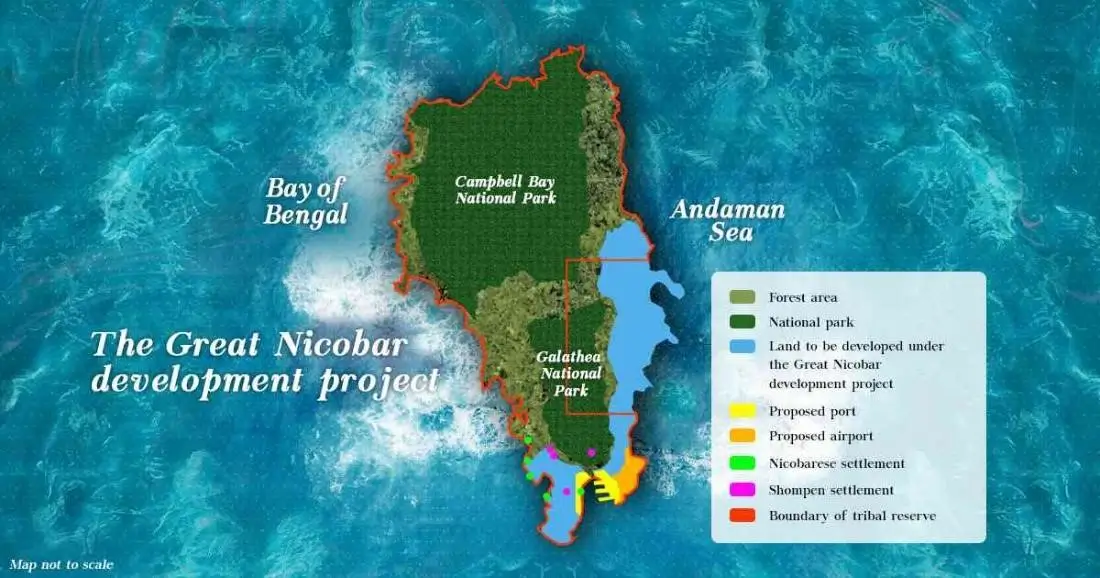
Great Nicobar Unleashed: Rs 80,000 Cr Eco-Strategic Pivot
NGT’s February 16 ruling upheld 2022 clearances for the holistic development on 910 sq km Great Nicobar, including a world-class transshipment port, international airport, township for 15,000, and 450 MVA power plant. Valued at Rs 80,000+ crore, it eyes Southeast Asia hub status, handling 25 million TEUs annually.
A high-powered committee addressed coral protection, single-season data gaps, and ICRZ compliance. Tribunal mandated “full and strict” adherence to conditions safeguarding Shompen/Nicobarese tribes, leatherback turtles, and rainforests. Strategic port reduces Colombo/Singapore dependency, boosting logistics by 30%.
Economic Tsunami: Jobs, Growth, and Connectivity
High-speed rails promise 50,000+ jobs in manufacturing alone, slashing travel times—Delhi-Varanasi in 3 hours. Nicobar could generate 40,000 direct employments, GDP uplift via tourism, fisheries, and exports. Together, they propel Viksit Bharat@2047, enhancing tourism in Andamans and freight efficiency.
Challenges persist: rail land hurdles, Nicobar’s tribal sensitivities. Yet, safeguards like HPC oversight and tech transfers mitigate risks, positioning India as infra superpower.
As prototypes roll out and shovels hit Nicobar soil, India’s infra narrative shifts from vision to velocity—promising equitable prosperity.
Future Roadmap: Timelines and Watchpoints
BEML delivery: End-2026; Full corridors: 2029-2030. Nicobar: Stage-II forest nod pending, construction imminent post-compliance. Monitoring via NGT directives ensures sustainability.
These strides exemplify bold governance, balancing eco-stewardship with strategic imperatives for a resurgent India.







